Overdose Response Strategy Cornerstone Report Recommends Methods for Reducing Drug Overdoses in Jails
Four strategies for reducing overdose, recidivism, and improving jail staff morale examined in-depth
The Overdose Response Strategy (ORS) is a public health/public safety collaboration between the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and 21 High Intensity Drug Trafficking Areas (HIDTAs), including the Washington/Baltimore HIDTA. The partnership aims to reduce overdose (OD) by developing and sharing information across agencies and assisting communities with the implementation of evidence-based strategies.
Each year, the ORS completes a Cornerstone Project that focuses on a different priority topic. Recently, the ORS released its 2019 Cornerstone Report, which concentrates on preventing OD in jails. The Report’s primary audience is jail administrators who are interested in learning more about OD prevention, saving lives, or initiating or improving OD prevention services. It underscores that jails are part of a continuum of criminal justice interventions and explains that they are part of community in which multiple opportunities to reduce OD exist.
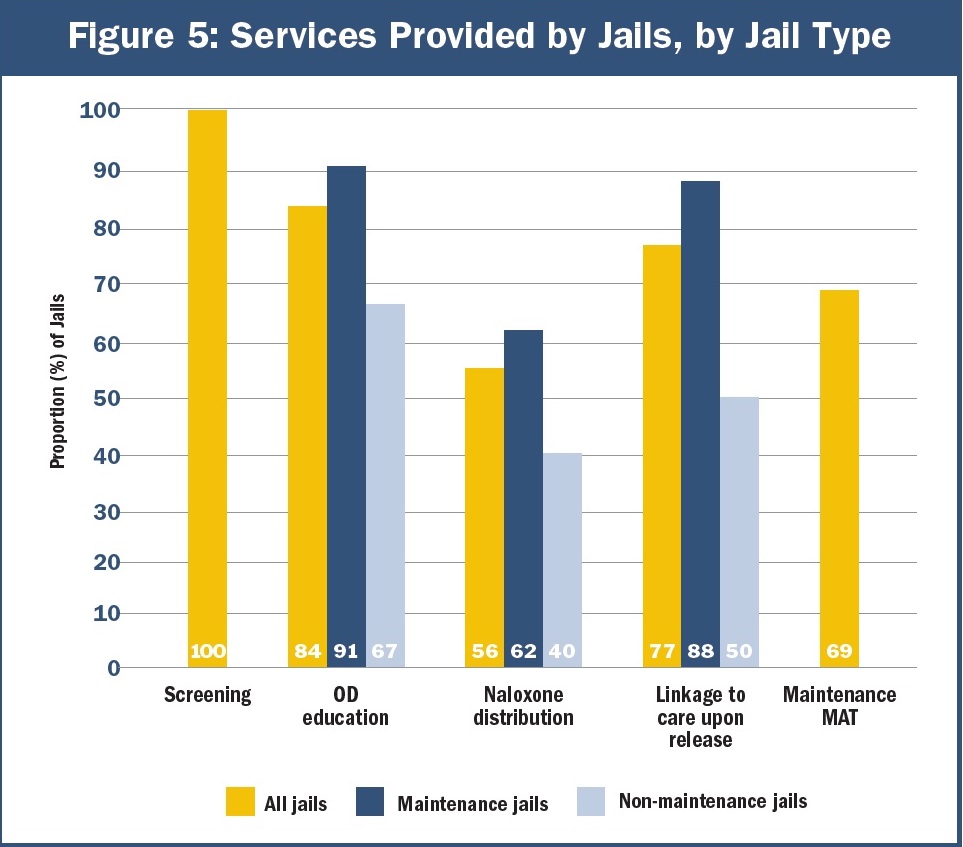
The 2019 Cornerstone Project examines four evidence-based services provided in 36 jails serving counties with a particularly high rate of opioid OD. Researchers conducted individual or small group interviews in 33 jails. They administered surveys with 483 jail staff in 24 jails. Additionally, the conducted interviews and surveys in 21 jails.
The four services the study examines are:
- Screening for substance use disorder (SUD)—intake procedures to identify SUD and other medical needs
- OD education and naloxone distribution (OEND)—education about OD risk factors and effective response, and provision of 1-2 doses of naloxone (an opioid antagonist medication that can reverse a potentially fatal OD with timely administration)
- Linkage to care upon release—direct assistance connecting individuals with drug treatment and other services post-incarceration, excluding passive referrals
- Maintenance medication-assisted treatment (maintenance MAT)—provision of MAT throughout incarceration
The Report’s goal of advancing the implementation of OD prevention services across jails nationwide is achieved by:
- Exploring all associated barriers, challenges, solutions, and successes, including real-life examples from the perspectives of service providers
- Featuring recommendations, troubleshooting, and lessons learned
Key takeaways from the Report include:
- Concerns about cost and diversion are manageable.
- Non-maintenance jails may be open to and interested in providing MAT than before.
- Support from security staff is essential.
- Availability of services in the community is key.
- Collaboration with community partners is essential.
To access the Report summary, click here
To access the entire Report, click here
